What causes bleeding during pregnancy? Is vaginal bleeding normal during pregnancy? When should you be worried about vaginal bleeding in pregnancy? Such questions about vaginal bleeding during pregnancy are bound to be scary. However, find solace in the fact that bleeding during pregnancy isn’t always a sign of trouble. But heavy bleeding or bleeding that’s accompanied by pain might indicate a complication. Let’s understand about vaginal bleeding in pregnancy and when to worry about it.
Bleeding during pregnancy
If you are pregnant, bleeding can happen from conception to delivery. Bleeding can occur early or later in pregnancy. Bleeding in early pregnancy is common; in many cases, it does not signal a major problem. Bleeding later in pregnancy can be more serious. You need to pay attention to the timing and type of bleeding you are experiencing to be able to report back to your doctor. Make sure to never leave bleeding in pregnancy unreported.
What is Spotting in Pregnancy?
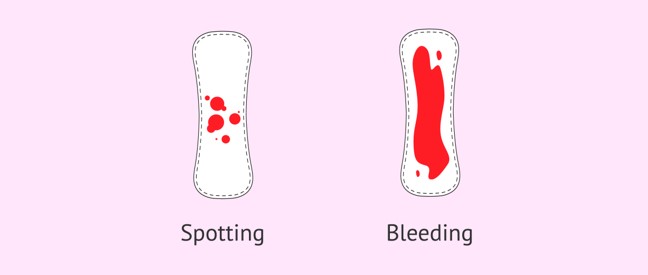
Tell me the difference between spotting and bleeding?
Spotting is a type of light bleeding. You may see just a few drops of blood in your underwear or if you wipe yourself with tissue and you see a little blood on the paper.. On the other hand, heavy bleeding will require a sanitary pad to protect your clothing.
Vaginal Bleeding in early pregnancy
Light amounts of vaginal bleeding early in your pregnancy can occur. In most cases, it’s not serious. It can happen in the first 20 weeks for different reasons. It can be the result of something serious or non-serious. Continued bleeding throughout the pregnancy is not common.
Vaginal Bleeding during the first trimester
Bleeding in the first trimester happens to about 15–25% of pregnant women says ACOG. ‘Light bleeding or spotting can occur 1–2 weeks after fertilization when the fertilized egg implants in the lining of the uterus. The cervix may bleed more easily during pregnancy because more blood vessels are developing in this area. It is not uncommon to have spotting or light bleeding after sexual intercourse or after a Pap test or pelvic exam.’
A medical research [1] establishes that heavy bleeding in the first trimester, particularly when accompanied by pain, is associated with higher risk of miscarriage. Spotting and light episodes are not, especially if only lasting 1–2 days.
Bleeding in the Second and Third Trimesters
Vaginal bleeding, or bleeding per vaginam, in the second and third trimesters of pregnancy is less common than in
the first trimester but can similarly arise due to varied causes. The bleeding can widely range from
having vaginal bleeding for no identifiable reason—seen in approximately half of those with vaginal bleeding in
pregnancy [3]—to being the normal and expected bleeding with term labor, to having serious potential
consequences for both the mother and fetus.
What should I do if I have abnormal bleeding during pregnancy?
Abnormal bleeding in late pregnancy may be more serious because it can signal a problem with the mother or baby. Call your doctor as soon as possible if you experience any bleeding in your second or third trimester.
Finding out the cause of bleeding later in pregnancy
Common problems that may cause light bleeding later in pregnancy include inflammation of or growths on the cervix. Heavy bleeding is a more serious sign. Heavy bleeding may be caused by a problem with the placenta. Any amount of bleeding also may signal preterm labor. If you have any bleeding late in pregnancy, contact your ob-gyn right away or go immediately to the hospital.

Placenta problems that can cause bleeding in pregnancy
Several problems with the placenta later in pregnancy can cause bleeding, Your doctor is best qualified to identify and determine the cause and finalise the line of treatment and suggest you dos and don’ts accordingly. Most common ones being:
- Placental abruption
- Placenta Previa
- Placenta accreta
Can bleeding be a sign of preterm labor?
Late in pregnancy, vaginal bleeding may be a sign of labor. If labor starts before 37 completed weeks of pregnancy, it is called preterm labor. Other signs of preterm labor include the following:
- Change in vaginal discharge (it becomes watery, mucus-like, or bloody) or increase in amount of vaginal discharge
- Pelvic or lower abdominal pressure
- Constant, low, dull backache
- Mild abdominal cramps, with or without diarrhea
- Regular or frequent contractions or uterine tightening, often painless (four times every 20 minutes or eight times an hour for more than 1 hour)
- Ruptured membranes (your water breaks—either a gush or a trickle)
How preterm labor is managed is based on what is thought to be best for your health and your baby’s health. In some cases, medications may be given. When preterm labor is too far along to be stopped or there are reasons that the baby should be born early, it may be necessary to deliver the baby.
References: [1] Association Between First-Trimester Vaginal Bleeding and Miscarriage; Reem Hasan, Donna D. Baird, Amy H. Herring, Andrew F. Olshan, Michele L. Jonsson Funk, and Katherine E. Hartmann; Published in 2009 Oct; doi: 10.1097/AOG.0b013e3181b79796; https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2828396/ [3] Yang J, Hartmann KE, Savitz DA, et al. Vaginal bleeding during pregnancy and preterm birth. Am J Epidemiol; 2004;160:118-25. [4] Vahanian SA, Vintzileos AM. Placental implantation abnormalities: a modern approach. Curr Opin Obstet; Gynecol 2016;28:477-84.
